“I remember applying for a Permanent Residency when I was pursuing my MBA. My reasoning at the time was that I wanted a better lifestyle. I followed that plan and did a few jobs here in India. However, I didn’t get any satisfaction or happiness working with some of the start-ups here. My professional experiences with people, travelling challenges and the pollution in Delhi were major factors for me to move,” 34-year-old Sumit Kumar (name changed on request), who moved to Canada with his wife in February 2019, told The Quint.
Much earlier than Sumit, 46-year-old Aneesh Sinha (name changed on request) moved to Canada with his wife in 2003.
His story has a twist, though. He returned to India with his wife and two kids in 2007 after spending close to five years in Canada and obtaining Canadian citizenship.
He got a high-paying job, and a top post in India in the banking Industry, but something was missing.
Aneesh returned to Canada with his family in 2011.
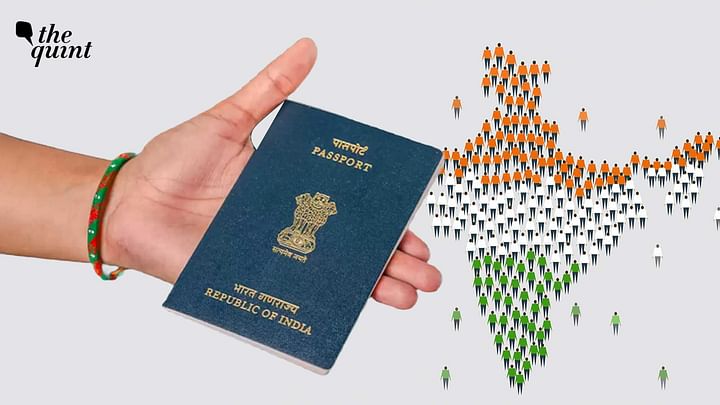
Sumit’s and Aneesh’s are just two cases from the long list of 8,81,254 Indians who have given up their citizenship since 2015, for different reasons, as per Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) data presented in the Lok Sabha in December 2021.
Not just them. This upward migratory trend or the ‘The Great Indian Migration’ also includes high net worth individuals, or HNIs, who have been increasingly renouncing Indian citizenship over the years for several reasons.
We take a detailed look.
8.81 Lakh Indians Renounced Citizenship in 7 Years
In response to a question in the Lok Sabha in December 2021, Minister of State for Home Affairs Nityanand Rai revealed that 8,81,254 people had given up their Indian citizenship between 1 January 2015 and 21 September 2021.
Rai told the parliament that according to the data available with the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), 1,33,83,718 Indians are now living in foreign countries.
Aneesh and Sumit, two MBA graduates, are also among the highly skilled Indians who chose to move abroad, highlighting another growing trend.
India Has the Highest Share of Highly Educated Emigrants
According to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) report published in February 2020, India has the largest high-skilled diaspora in the OECD area, with over 3 million tertiary-educated migrants.
The OECD currently has 38 member countries, including Australia, Canada, France, Germany, Netherlands, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, United States, among others.
According to InterNations, a Munich-based global social networking site for expat communities, “Indian expats are happier with their working hours and live-in countries where new concepts of work play a more important role than back home in India. Indians enjoy better working hours and a better work-life balance abroad.”
“Predictability of life, stability and a laidback lifestyle were my reasons in 2011. I worked on a lesser salary than what I was earning in India, but I was very happy. My work-life balance was such that I used to drop and pick up my kids from school. By 3.30 pm, we used to be together at home. This is the thing I was missing in India,” informed Aneesh.
“To be honest, I have not rued my decision since. I love the fact that I came back when I did. However, certain things about this country are not pretty. You have a mechanical life here, but it does leave you time with your loved ones. It takes time to get to that state of mind,” he added.
Among those migrating are also India’s super rich.
According to a Morgan Stanley report published in The Economic Times in 2018, India lost the highest percentage of dollar-millionaires to migration between 2014 and 2018 (a millionaire is defined as someone with wealth of $1 million or more).
Data compiled by the team headed by Ruchir Sharma, head of emerging markets and chief global strategist at Morgan Stanley Investment Management, showed that nearly 23,000 dollar-millionaires left the country between 2014 and 2018, with 7,000 leaving in 2017 alone. The 23,000 figure amounts to 2.1% of India’s rich, ahead of France’s 1.3% and China’s 1.1%.
“One likely reason that Indian millionaires are leaving is due to the anti-corruption and regulatory crackdown in India, resulting in wealthy Indians wanting to move their capital elsewhere,” Ruchir had told the Financial Express.
It is important to note here that on 8 November 2016, Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced ‘demonetisation’ to weed out black money from the country. The move wiped out 86% of India’s currency overnight, with the currency notes of Rs 500 and Rs 1,000 denominations getting banned.
China topped the list with 16,000 HNIs migrating, followed by India and Russia.
The report, however, said that there was an overall decline in the HNI migration numbers due to the coronavirus impact, adding that travelling/migrating was likely to be more complicated “due to ongoing quarantines and health checks in most countries.”
“Provisional estimates show a drop in inward and outward HNI migration for the year 2020 as many people have been unable or unwilling to move due to the coronavirus outbreak. Some have put off moving till a later date, whilst others have cancelled their plans to move altogether,” the Global Wealth Migration Review report said.
“It can also be sign of bad things to come as HNIs are often the first people to leave,” reads the report. For example, “Russia, Iran and Qatar, all have sanctions and embargoes to deal with and they have been losing HNIs to migration of late,” says the report.
Russia and Iran face sanctions from Western countries, while Qatar faces an embargo from the UAE, Egypt and Saudi Arabia.
In the case of Hong Kong, political instability has damaged the country long-term appeal.
Aneesh shared the story of his very close friend, who invested a large sum of money (Rs 90 lakh) to obtain Canadian citizenship in 2013 through a separate citizenship programme (As of 2022, an investment of CAD 1.2 million or Rs 7.27 crore is needed for a period of five years at no interest under one of the two available immigrant investor programmes).
“The catalyst for her was she and her husband just wanted a good life,” said Aneesh.
The ‘Golden Visa’ Route for Wealthy Indians
The ‘Golden Visa’ route is also a popular option among wealthy Indians. It means acquiring the residency, immigration, and citizenship of a country through investment. It opens several opportunities for families in terms of business, career, education, healthcare, tax, and lifestyle.
According to Henley and Partners, an investment firm working for residence and citizenship in the UK, the number of Indians inquiring about the Golden Visa route increased by 54 percent in 2021 from 2020. There was also a 63 percent increase in interest in investment migration shown by Indian nationals between December 2019 and December 2020.
[“source=thequint”]