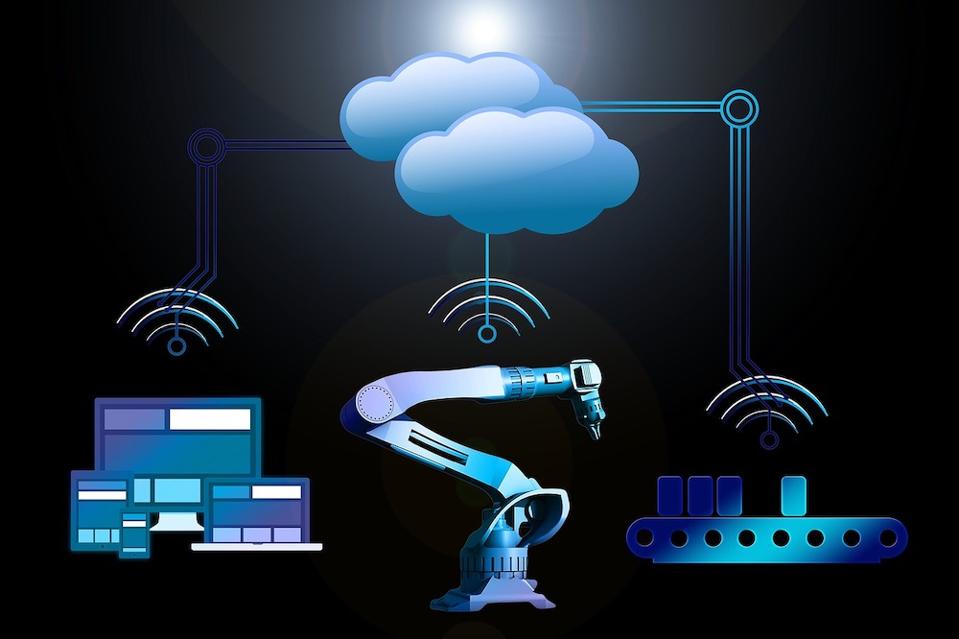
Two trends that are dominating the technology industry are the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). But for industrial automation, these two technologies are much more than the buzzwords or trending topics. The convergence of AI and IoT will redefine the future of industrial automation. It is set to lead the Industry 4.0 revolution.

Industry 4.0
SOURCE: PIXABAY
IoT and AI are two independent technologies that have a significant impact on multiple industry verticals. While IoT is the digital nervous system, AI becomes the brain that makes decisions which control the overall system. The lethal combination of AI and IoT brings us AIoT – Artificial Intelligence of Things – that delivers intelligent and connected systems that are capable of self-correcting and self-healing themselves.
To appreciate the promise of AIoT, we need to look at the evolution of connected systems.
Cloud computing provided three key aspects to connected systems – connectivity, storage, and compute. With an always-on architecture, cloud computing enabled multiple devices to seamlessly connect with each other. Apart from sending machine-to-machine (M2M) messages to each other, these devices sent telemetry data to the cloud that was ingested and stored centrally. The compute service in the cloud processed these large datasets representing the data from a diverse set of devices to derive insights.
Connectivity, storage, and compute became the foundation of the IoT. Initially, data was processed based on Big Data architectures such as Hadoop and Spark. IoT and Big Data helped stakeholders understand the patterns and the correlation between various devices and sensors. The outcome was presented in insightful visualizations and charts that were a part of IoT dashboards.
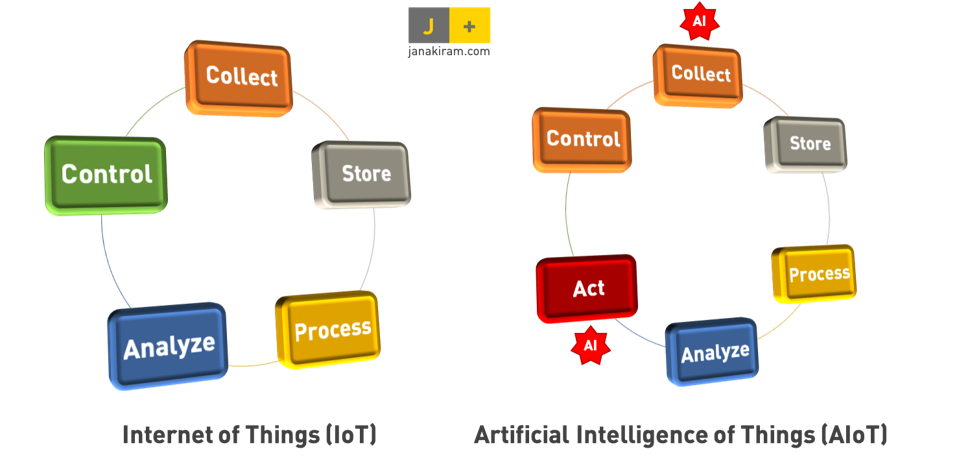
In summary, the first generation of cloud-based IoT provided five key capabilities:
Collect – Telemetry data from a large number of devices and sensors is collected at a central location.
Store – The telemetry data is stored in scalable storage systems such as data lakes.
Process – Big Data platforms are used to process and analyze the telemetry datasets.
Analyse – The insights from the Big Data systems were utilized to present the analysis through rich visualizations
Control – Device operators and field engineers control the devices based on the recommendations from Big Data systems.
By combining AI with industrial IoT, we add an important ability to connected systems – Act.
AI goes beyond the visualizations by acting on the patterns and correlations from the telemetry data. It plugs the critical gap by taking appropriate actions based on the data. Instead of just presenting the facts to humans to enable them to act, AI closes the loop by automatically taking an action. It essentially becomes the brain of the connected systems.
AIoT
SOURCE: JANAKIRAM MSV
AI is going to supercharge industrial IoT at two different levels. Firstly, it impacts the telemetry data by augmenting the sensors with intelligence. Secondly, AI will be used to analyze the inbound telemetry data stream in real-time or in batch mode. It plugs itself into the start (devices) and the end (analysis) of the IoT spectrum.
For example, a camera that is treated as an image sensor will send every frame to the IoT system to analyze the feed for certain objects. By applying AI to the camera device, it sends the frame only when a specific object is detected. This significantly speeds up the process while saving the CPU from processing every frame. The same principle may be applied to speech synthesis and other forms of telemetry data. AI-enabled sensors are the future of IoT systems. Smart cameras powered by AI accelerators from Intel, NVIDIA and Qualcomm will soon become the standard image sensors.
By applying deep learning models based on neural networks to incoming sensor telemetry data, sophisticated IoT systems will be able to find anomalies in real-time. When a critical error is predicted by the neural network, the faulty device may be shut down to avoid a fatal accident or an event. The key difference between existing rules engine of IoT and AIoT lies in being proactive vs reactive. Current IoT systems are designed to react to an event while AIoT systems can proactively detect failures and events. The infusion of AI in IoT systems delivers the promise of predictive maintenance which will help organizations save millions of dollars in support and maintenance of equipment.
The future of industrial automation lies in the convergence of AI and IoT. Artificial Intelligence of Things will impact almost every industry verticle including automotive, aviation, finance, healthcare, manufacturing and supply chain.
[“source=forbes”]